At the end of May, India joined
the First Movers Coalition
, a global initiative aimed at decarbonising heavy industries and long-distance transport. This is important because transportation is one of the sectors where emissions are growing fastest in India. Already transport emissions are around 14 per cent of India’s total CO2 emissions, and 90 per cent of transport emissions are from road transport. Thus, decarbonising road transport is vital, including for
India’s pledge
to achieve net-zero emissions by 2070. A strong decarbonisation target for the transport sector, especially the road sector, will also bring significant co-benefits like cleaner air and healthier people. To set and achieve such a decarbonisation target, it is necessary to have a realistic estimate of current energy use and emissions from road transport. From this, future projections can be made that help inform and illuminate policy courses for the country. Recent
research by ICCT
looked at eight leading models that have attempted to estimate future emissions from India’s transport sector and the findings are significant. Let’s discuss three important takeaways: Vehicle emissions will continue to rise if nothing is done All of the models indicated an unabated rise in vehicle emissions in the future if no policy improvements are made. This is despite the significant differences in key assumptions revealed by the meta-analysis, including with respect to vehicle activity level, energy used by the sector, fuel consumption, and emission levels from various vehicle transport modes. Even still, they all agree that total sector emissions will rise, rather than decline, absent additional policy action. [caption id=“attachment_10974251” align=“alignnone” width=“640”]
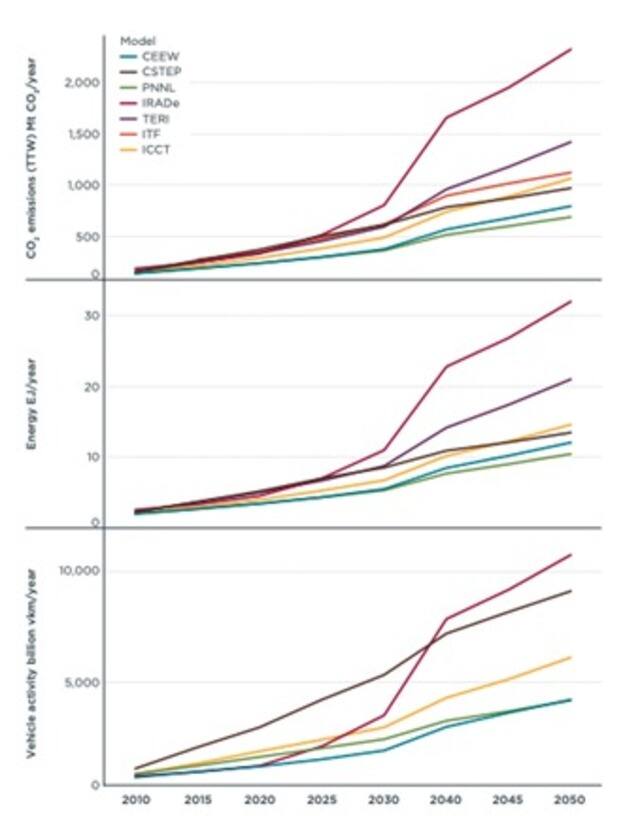 Figure 1: The different models estimate key trends under Business as Usual (BAU) scenarios for India’s road transport sector.
Figure 1: The different models estimate key trends under Business as Usual (BAU) scenarios for India’s road transport sector.
Source: ICCT[/caption] Note, too, that these variations in data affect our understanding of present emissions and mean there is significant uncertainty regarding future emission levels for the Indian road transport sector. The current lack of data about travel patterns and how they have been changing over time can be addressed by institutionalising data collection for the transport sector. Government bodies can organise collection of this data, including by initiating periodic national-level travel surveys and an annual greenhouse gas emissions inventory. COVID-19 impacted road transport In almost all countries, the COVID-19 pandemic led to lockdowns that restricted human activities and movements to minimise the spread of the virus. Even though India’s motor vehicle fleet has grown tremendously in the last few decades, the lockdown significantly affected both travel and vehicle sales, and the latter dropped by approximately 14 per cent in 2020 after dropping about 18 per cent in 2019. Additionally, based on end-use petroleum consumption, the
ICCT has estimated
there was at least an 11 per cent reduction in travel demand in 2020 as compared to 2019. [caption id=“attachment_10974301” align=“alignnone” width=“640”]
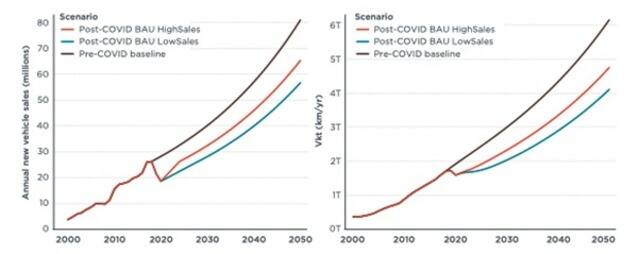 Figure 2. Vehicle sales and vehicle activity under pre- and post-COVID-19 BAU scenarios
Figure 2. Vehicle sales and vehicle activity under pre- and post-COVID-19 BAU scenarios
Source: ICCT[/caption] In exploring the impact of the pandemic by considering future sales trajectories, the study indicated that future vehicle sales expected under both high- and low-sales scenarios are significantly lower than the sales projected under the pre-COVID future scenario. Indeed, the post-COVID analysis showed a reduction in CO2 emissions of around 30 per cent and 42 per cent in 2050 under the high- and low-sales scenarios, respectively. Cleaner transport is possible with existing strategies The government of India has set economy-wide emissions reduction targets, but recall that there are not yet goals for any specific sectors. India needs a strong decarbonisation target specifically for the road transport sector to help achieve its climate, air quality, and public health goals. The ICCT study envisaged and analysed High Ambition and Aggressive Policy scenarios for India to 2050 that align the country closer to path that limits warming to 1.5°C. These scenarios include efficiency improvement in petrol and diesel motor vehicles, vehicle electrification with a low-carbon grid, increased use of alternative fuels, mode shift from private vehicles to public transport, and mode shift from road freight to electric rail. [caption id=“attachment_10974311” align=“alignnone” width=“566”]
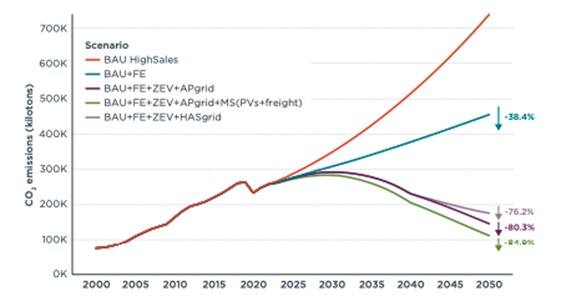 Figure 3. CO2 emissions reduction offered by different policy interventions in an Aggressive Policy scenario under high vehicle sales.
Figure 3. CO2 emissions reduction offered by different policy interventions in an Aggressive Policy scenario under high vehicle sales.
Note: AP: Aggressive Policy scenario; HAS: High Ambition Scenario, FE: ICE vehicle fuel efficiency improvement, ZEV+grid: Vehicle electrification along with grid decarbonization; MS (PVs+freight): Mode shift (Private vehicles to buses and HDT to electric rail)
Source: ICCT[/caption] Results indicate that India could lower emissions from the road transport sector by at least 25 per cent (High Ambition path) or 50 per cent (Aggressive Policy path) by 2050, compared to 2020 levels. India can also reverse the growth in emissions if it undertakes aggressive actions for vehicle electrification with continued efficiency improvements in petrol and diesel motor vehicles until 2050. India does not currently have a sector-specific target for transport as part of its Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC) under the Paris Agreement. However, the Paris commitment cannot be met without contribution from the transport sector, and as we’ve shown, India can be confident in setting a target to lower emissions from road transport by 25 per cent to 50 per cent by 2050 in comparison to 2020. ICCT research shows that achieving such emissions reduction is possible, and this will not only help achieve climate goals, but also improve the health of all people in India. Amit Bhatt is Managing Director (India) for the International Council on Clean Transportation (ICCT). His Twitter handle is @amitbhatt4u. Namita Singh is Associate Researcher (Consultant) for the International Council on Clean Transportation (ICCT). Views expressed are personal. Read all the Latest News
, Trending News
, Cricket News
, Bollywood News
, India News
and Entertainment News
here. Follow us on
Facebook
,
Twitter
and
Instagram
.
Why decarbonising India’s road transport is vital for achieving climate goals
Amit Bhatt and Namita Singh
• July 28, 2022, 20:43:19 IST
Currently, transport emissions are about 14 per cent of India’s total CO2 emissions, and 90 per cent of transport emissions are from road transport
Advertisement
)
End of Article