Following the tragic killing of a 17-year-old near Paris earlier this week, France has found itself at the centre of a global debate over police violence.
Protests
have broken out in a number of places, with some turning violent as protestors set fire to cars, garbage, and buildings. The shooting of the teen, identified as Nahel, was captured on video and shocked the country. Many in France see Nahel’s killing as a reflection of racism against Arab and Black communities in the country, given that it’s not the first time something like this has happened. The killing also has raised questions about whether France has failed to move on since it was wracked by weeks of urban rioting in 2005. It stirred up long-simmering tensions between police and young people in disadvantaged neighbourhoods. It also prompted calls for a thorough overhaul of the conditions governing the use of weapons by police. Shooting on the rise Thirteen people were killed in police shootings last year after not complying with orders during traffic stops, according to police. This year, three people, including Nahel — who failed to stop when ordered to — have died in similar circumstances.
Also Read: France unrest: Policeman who killed teen says sorry as violence intensifies
More generally, the number of people killed by police officers after they refused to comply with an order is on the increase. In 2021, according to police figures, four people had been killed in such circumstances. Blame the law In the hours that followed the death of Nahel, the president of France’s lower house of parliament, Yael Braun-Pivet, said that she’s ready to reassess how a law governing gun use by police is being implemented. It was adopted in 2017, in the wake of a series of extremist attacks in France. Since then, law enforcement officers can shoot at a vehicle when a driver fails to comply with an order, and when it is likely to endanger their lives or those of others. In the case of Nahel, the officer who fired the fatal shot will be investigated for voluntary homicide after an initial investigation concluded that “the conditions for the legal use of the weapon were not met.” Before the law was introduced, police officers had to prove self-defence to justify the use of a gun. Since it took effect, they have been authorised to fire on a vehicle “whose occupants are likely to perpetrate, in their flight, attacks on their life or physical integrity or that of others.” The internal security code, however, stipulates that the use of weapons is authorised only in cases of “absolute necessity and in a strictly proportionate manner.” [caption id=“attachment_12810062” align=“alignnone” width=“640”]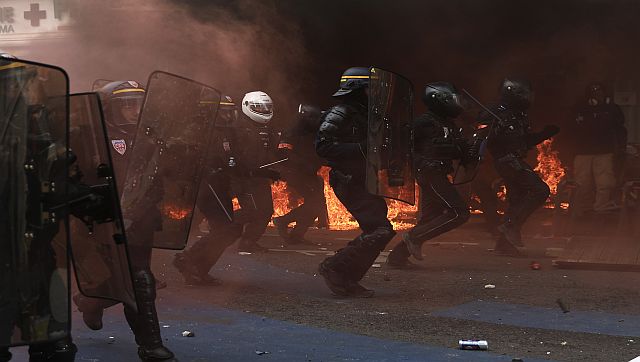 Riot police officers run next to a fire set in front of a building during a demonstration in Paris. AP[/caption] Researchers Sebastian Roché, Paul le Derff and Simon Varaine, who have produced a statistical analysis linking the increase in the number of deaths to the law, said a similar rise in deaths by shooting didn’t occur in neighbouring countries. They have also questioned the lack of appropriate training for police officers. “There’s a very clear correlation between this change in the law in 2017 and the rise in fatal police shootings,” Roché told Le Nouvel Obs media. “On average, there are 25 per cent more shootings, and five times more lethal shootings. Since 2017, there has been a clear shift in police practices towards an increase in police shootings.” A French problem In addition to the lethal shootings, French police have also been regularly criticised for their violent tactics. During the
yellow vest protests
that started in 2018, a top European official criticised French authorities for their handling of the anti-government protests that rocked the country for months, urging them to “show more respect for human rights.”
Also Read: How shooting of 17-year-old has led to protests and violence
French police were also harshly criticised for their handling of the 2022 Champions League final that took place at the Stade de France, which is located in the Saint-Denis suburb. Police used tear gas on fans who were stuck in congested, slow-moving lines for hours before the game, which was eventually delayed by about 40 minutes. More recently during a wave of demonstrations against the raise of the
retirement age
, French police were hit by claims they were too tough on protesters. Amnesty International, the International Federation of Human Rights and the Council of Europe — the continent’s main human rights body — are among organisations that cited excessive use of force by French police. Past riots The unrest in French suburbs that started following Nahel’s death is not unprecedented. [caption id=“attachment_12810072” align=“alignnone” width=“640”]
Riot police officers run next to a fire set in front of a building during a demonstration in Paris. AP[/caption] Researchers Sebastian Roché, Paul le Derff and Simon Varaine, who have produced a statistical analysis linking the increase in the number of deaths to the law, said a similar rise in deaths by shooting didn’t occur in neighbouring countries. They have also questioned the lack of appropriate training for police officers. “There’s a very clear correlation between this change in the law in 2017 and the rise in fatal police shootings,” Roché told Le Nouvel Obs media. “On average, there are 25 per cent more shootings, and five times more lethal shootings. Since 2017, there has been a clear shift in police practices towards an increase in police shootings.” A French problem In addition to the lethal shootings, French police have also been regularly criticised for their violent tactics. During the
yellow vest protests
that started in 2018, a top European official criticised French authorities for their handling of the anti-government protests that rocked the country for months, urging them to “show more respect for human rights.”
Also Read: How shooting of 17-year-old has led to protests and violence
French police were also harshly criticised for their handling of the 2022 Champions League final that took place at the Stade de France, which is located in the Saint-Denis suburb. Police used tear gas on fans who were stuck in congested, slow-moving lines for hours before the game, which was eventually delayed by about 40 minutes. More recently during a wave of demonstrations against the raise of the
retirement age
, French police were hit by claims they were too tough on protesters. Amnesty International, the International Federation of Human Rights and the Council of Europe — the continent’s main human rights body — are among organisations that cited excessive use of force by French police. Past riots The unrest in French suburbs that started following Nahel’s death is not unprecedented. [caption id=“attachment_12810072” align=“alignnone” width=“640”] Riot police officers detain a protester during a demonstration in Lille, northern France. AP[/caption] Back in 2005, the electrocutions of Zyed Benna, 17, and Bouna Traore, 15, after they hid from police in a power substation in the Paris suburb of Clichy-sous-Bois sparked three weeks of rioting throughout France. The nationwide riots raged through housing projects in troubled neighbourhoods with large minority populations. Although they stemmed from the teens’ deaths, they were fuelled by deeper problems of discrimination, unemployment and a sense of alienation from French society. What comes next Nearly two decades later, those problems and that sense of injustice remain deeply rooted in French society. The response to the riots might be different, though. There was no video in 2005 and rioting didn’t spread as quickly as this time. Social media also amplified the latest killing. But while in 2005, the French government increased anger with a brutal response under a state-of-emergency law, French president Emmanuel Macron has been careful not to antagonise anyone in a bid to avoid an explosion of violence. Macron’s first reaction was to say that Nahel’s death was “inexcusable.” The video made it impossible for him and his ministers to argue that the shooting was justified. However, during the first two nights of riots, police officers have showed restraint in their use of force. In addition, the judicial decision to hand a preliminary charge of voluntary homicide to the main suspect, and to keep him in detention, could help ease tensions. With inputs from AP Read all the Latest News
, Trending News
, Cricket News
, Bollywood News
, India News
and Entertainment News
here. Follow us on
Facebook
,
Twitter
and
Instagram
.
Riot police officers detain a protester during a demonstration in Lille, northern France. AP[/caption] Back in 2005, the electrocutions of Zyed Benna, 17, and Bouna Traore, 15, after they hid from police in a power substation in the Paris suburb of Clichy-sous-Bois sparked three weeks of rioting throughout France. The nationwide riots raged through housing projects in troubled neighbourhoods with large minority populations. Although they stemmed from the teens’ deaths, they were fuelled by deeper problems of discrimination, unemployment and a sense of alienation from French society. What comes next Nearly two decades later, those problems and that sense of injustice remain deeply rooted in French society. The response to the riots might be different, though. There was no video in 2005 and rioting didn’t spread as quickly as this time. Social media also amplified the latest killing. But while in 2005, the French government increased anger with a brutal response under a state-of-emergency law, French president Emmanuel Macron has been careful not to antagonise anyone in a bid to avoid an explosion of violence. Macron’s first reaction was to say that Nahel’s death was “inexcusable.” The video made it impossible for him and his ministers to argue that the shooting was justified. However, during the first two nights of riots, police officers have showed restraint in their use of force. In addition, the judicial decision to hand a preliminary charge of voluntary homicide to the main suspect, and to keep him in detention, could help ease tensions. With inputs from AP Read all the Latest News
, Trending News
, Cricket News
, Bollywood News
, India News
and Entertainment News
here. Follow us on
Facebook
,
Twitter
and
Instagram
.
Explained: How the killing of a teenager puts spotlight on police violence in France
FP Explainers
• June 30, 2023, 16:23:51 IST
France is in upheaval over the shooting of a 17-year-old boy, identified as Nahel. The incident has not only stirred up long-simmering tensions between cops and young people, but also put a spotlight on police violence in the country
Advertisement
)
End of Article