Akamai Technologies, Inc., the provider of cloud services for delivering, optimising and securing online content and business applications, released its Fourth Quarter, 2013 State of the Internet Report. Based on data gathered from the Akamai Intelligent Platform, the report provides insight into key global statistics such as network connectivity and connection speeds, attack traffic, broadband trends and availability, and IPv6 adoption. It also includes measurements of page load times using Akamai’s real user monitoring (RUM) capabilities, and provides insights on Akamai traffic activity related to Internet disruptions in Syria, Suriname, Guyana, Libya and Cuba.
Highlights from Akamai’s Fourth Quarter, 2013 State of the Internet Report:
Global Average and Average Peak Connection Speeds
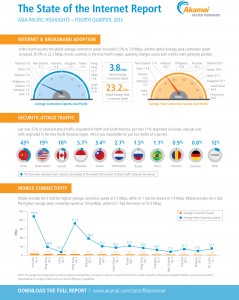
The global average connection speed continued to improve, with a quarterly increase of 5.5 percent, reaching 3.8 Mbps. Despite this improvement, half of the countries/regions listed among the top 10 in global average connection speeds - including the top four countries/regions - actually saw nominal declines quarter-over-quarter, ranging from a loss of 0.7 percent in the Netherlands to a drop of 6.7 percent in Latvia. Despite a 1.1 percent decline in average connection speed, South Korea held the top spot from quarter to quarter, reporting the highest average connection speed of 21.9 Mbps.
[caption id=“attachment_83085” align=“aligncenter” width=“239”]  State of the Internet[/caption]
Interestingly, quarterly increases seen in Ireland (8.4 percent increase to 10.4 Mbps) and the United States (2 percent increase to 10 Mbps) helped push both countries to average connection speeds of 10 Mbps or more, marking the first time that all of the top 10 countries/regions had average connection speeds at/above the “high broadband” threshold.
Overall, 133 qualifying countries/regions ended the year with higher average connection speeds than the year before, contributing to an increase of 27 percent from the end of 2012. Both South Korea and Ireland experienced year-over-year growth of more than 50 percent, at 57 percent and 59 percent, respectively. The smallest yearly increase among the top 10 was seen in Latvia, which added 11 percent during the course of 2013.
Global average peak connection speeds recovered from a small decline in the third quarter of 2013 with impressive improvement of 30 percent to 23.2 Mbps in the fourth quarter. A total of 138 qualifying countries/regions - and all of the top 10 - experienced higher average peak connection speeds than in the third quarter, with increases ranging from 1.3 percent in South Korea to 179 percent in Libya, which improved to 15.8 Mbps. Hong Kong and South Korea boast the highest average peak connection speeds and remain the only two countries/regions above 60 Mbps, at 68 Mbps and 64.4 Mbps, respectively.
Year over year, the global average peak connection speeds increased 38 percent compared to the fourth quarter of 2012. In total, 134 countries/regions experienced annual improvement in average peak connection speeds, ranging from 2.5 percent in Chile (to 20.3 Mbps) to 163 percent in Uruguay (to 36.7 Mbps). The country with the lowest average peak connection speed was Iran, at 5.5 Mbps, which was up 20 percent from the third quarter and 103 percent year over year.
Global high broadband (>10 Mbps) adoption rates in the fourth quarter slowed from previous, double-digit percentage growth to a quarterly increase of 1.6 percent, staying at 19 percent. Year-over-year improvement was strong, however, with the global high broadband adoption rate increasing by 56 percent from the fourth quarter of 2012.
Quarter-over-quarter, the global broadband adoption rate grew 4.3 percent, with 55 percent of all connections to Akamai taking place at speeds of 4 Mbps or above. South Korea and Switzerland topped the list at 94 percent and 91 percent adoption, respectively. By the end of 2013, a total of 83 qualifying countries/regions experienced year-over-year growth in their broadband adoption rates. This resulted in global broadband adoption growing 27 percent year-over-year in 2013.
“We’ve reached a significant milestone in the improvement of average connection speeds,” said David Belson, editor of the State of the Internet Report. “The fact that all of the top 10 countries/regions’ average connection speeds are now at or exceeding the high broadband threshold - and continued strong growth in countries like South Korea and Ireland - is indicative of the progress that’s being made in broadband penetration. It’s reasonable to expect these promising trends will continue to be reflected in future reports.”
Global Internet Penetration
In the fourth quarter of 2013, more than 780 million IPv4 addresses from 238 unique countries/regions connected to the Akamai Intelligent Platform. This translates to nearly 3 percent more than in the third quarter and 10 percent more than in the fourth quarter of 2012.
Quarterly growth was also seen in eight of the top 10 countries/regions, with the greatest increase once again seen in Brazil, which added nearly 8 percent (or approximately 2.7 million IPv4 addresses).
IPv6 Adoption
The United States and select European countries continue to lead the world in terms of IPv6 adoption, with Europe again having seven of the top 10 leading countries. Japan and Peru are the only countries from their respective regions to make the top 10 list. Double-digit percentage growth rates were seen in eight of the top 10 countries, with Peru and Germany seeing the largest increases, at 41 percent and 43 percent, respectively. The lowest rate of growth was seen in Romania, which increased by nearly 8 percent quarter-over-quarter.
Colleges and universities continue to be early adopters of IPv6, with moderate to large quarterly increases in adoption rates seen across most of the top 10. Iowa State, the University of Vienna Austria and the University of Saskatchewan all saw double-digit quarterly percentage increases.
Mobile Connectivity
In the fourth quarter of 2013, average connection speeds on surveyed mobile network providers ranged from a high of 8.9 Mbps (Russian mobile provider RU-1) down to a low of 0.6 Mbps (mobile provider ZA-1 in South Africa). The high is down just slightly from the 9.5 Mbps reported in the third quarter of 2013.
Akamai also conducted a fourth-quarter analysis of Akamai IO data to determine which user agents were used most frequently for mobile traffic requests. Based on data collected from a sample of requests from mobile devices to the Akamai Intelligent Platform over cellular networks, Android Webkit accounted for approximately 35 percent of requests and Apple Mobile Safari trailed at more than 29 percent of traffic. However, for traffic from mobile devices on all networks (not just cellular networks), Apple Mobile Safari was responsible for more than 47 percent of requests, while Android Webkit drove only 32 percent of requests.
Based on traffic data collected by Ericsson, the volume of mobile data traffic increased by 70 percent from the fourth quarter of 2012 to the fourth quarter of 2013, and grew approximately 15 percent between the third and fourth quarters of 2013.


)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)



