By Ranjeet S Mudholkar
Financial decision making is a crucial factor in the life of an individual as it has got the potential to affect many aspects of life; therefore it is very important that these decisions are taken in a prudent manner. There are several surveys that demonstrate people spend a lot of time in buying consumer and electronic goods such as mobile phone, refrigerator, television etc or even clothing and other accessories but little on buying a financial product. This calls for suitable attention towards one’s own purpose and attitude towards money and setting up right financial goals.
The income one earns goes towards current expenditure, saving for future and paying off the debt one has undertaken to acquire some assets. The financial decisions one is faced with lie in one of the above mentioned areas and if taken rationally would ensure that one leads a life that is free from financial anxiety.
[caption id=“attachment_730959” align=“alignleft” width=“380”] Rationality is defined as a state of having good sense and sound judgement and it is required to be exercised in every aspect of life. AFP[/caption]
Rationality is defined as a state of having good sense and sound judgement and it is required to be exercised in every aspect of life. AFP[/caption]
The next question is how to ensure it. And the answer is by applying rationality. Of the many items in the current expense list, some could be termed as necessary while the others could be on the discretion of the individual. The discretionary items could include things like luxury car which one fancies or a famous diamond which one would want to acquire for the purpose of glory. Applying sense to these financial decisions may be termed as rationality.
Rationality is defined as a state of having good sense and sound judgement and it is required to be exercised in every aspect of life. No financial decision is independent; the decisions are interdependent on one another. Increase in financial outlay on one may mean cut down on another. The impact may be immediate or might take some time to show. Thus it becomes very important to exercise rationality and keep all the financial goals in sight at the time of making a financial decision.
Financial planning is an approach that may infuse a sense of rationality in the entire financial decision making process. It advocates goal based approach for the management of finances of an individual through a clearly defined process.
Principles of Financial Planning
There are certain ground principles of financial planning with reference to the above mentioned division of income which if followed will ensure that one is able to manage his financial life smoothly
1. Net after-tax Income of an individual should be divided into three equal parts, to meet current expenses, to repay debt and to invest for the future.
2. Debt should not be taken for acquiring a depreciating asset. An example could be buying a mobile phone on loan.
3. There should be a limit on the expenditure which do not have salvage value e.g. holidays.
Behavioural Finance
Exercising rationality is important in financial markets and behavioural finance is a comprehensive field of study in personal finance. The proponents of behavioural finance, which is an evolving discipline, say that investors are human beings who are subject to range of emotions and information processing errors that may push them to make sub-optimal trading decisions. This leads to mispriced assets and inefficient markets, thus investors who understand and avoid these mistakes could exploit the resulting inefficiencies and end up earning excessive returns. As per a research conducted by Dalbar a US-based research and consulting firm, it was observed that average equity investors earned a return of just 3.83 percent per annum against the S&P 500 benchmark returns of 9.14 percent for a 20-year period ending December 2010.
Retail investors often make investment decisions based on herd mentality, i.e., they invest when the market is in bull phase. The idea of long term investment is yet to be accepted broadly by the Indian investor mindset. Financial planning could help alter this behaviour by making them invest as per long-term financial goals.
Financial inclusion
It is very important to note that individual financial rationality cannot be established without the entire financial ecosystem being put right in place. This calls for effective market participation by all the stakeholders, effective regulations, ethical behaviour and the financial goals to be established in order.
Tax Optimisation
It also helps an individual rationalise the tax liability by taking maximum benefits as provided in the Income Tax Act, 1961 like section 80C which provides for deductions from the income and Section 24, under which interest on housing loan can be deducted from taxable income up to a limit of Rs 150,000 for a self occupied house property while there is no limit if the house is let out on rent.
Take the case of a 36-year-old who has an income of Rs 12 lakhs per annum and lives in self-owned house, wife is a homemaker and child is 4 years old. He has investments in debt, equity at reasonable level, owns a small car but aspires to buy a bigger car, the needs as per the clients and the rationalised needs as per the planner are mentioned in the table below.
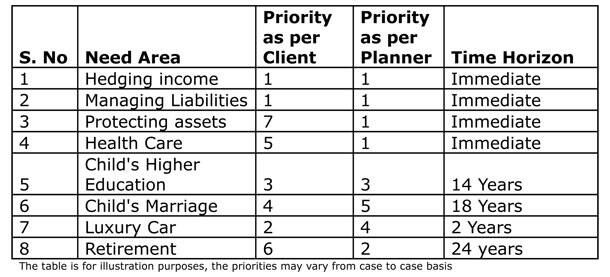
Thus we can see that all the goals can be managed simultaneously if the Financial Planning approach is applied , with the next steps being estimating implementing and monitoring the planning recommendations. This will ensure that rationality is exercised in all the major financial decisions and will result in financial worry free life of an individual. To achieve the same the services of an expert like a certified financial planner (CFP) professional is warranted who is equipped for the same.
The writer is working with Financial Planning Standards Board India (FPSB India) in the capacity of Vice Chairman and Chief Executive Officer. The views expressed here are personal, and do not necessarily represent that of the organization.
)