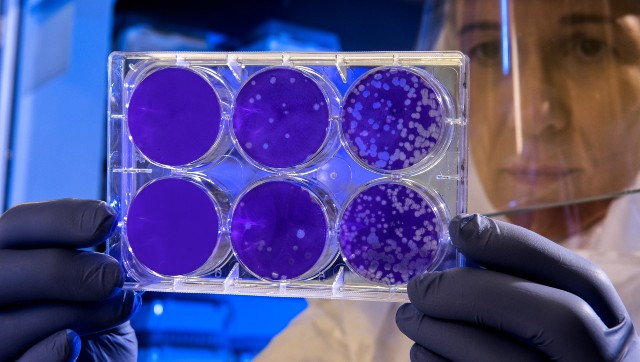
Antibiotics are drugs that are used to treat bacterial infections. These compounds kill bacteria or prevent them from multiplying thus helping eliminate the bacteria from the body. Millions of lives have been saved with the help of antibiotics over the last century — since the first antibiotic, penicillin was discovered. However, over time, many bacteria have developed resistance to existing antibiotics. Infections caused by antibiotic-resistant bacteria are hard to treat and often lead to severe conditions. Experts all over the world are trying to find solutions to this problem. Now, a group of researchers at the University of Göttingen, Germany, say that antivitamins can be used to treat bacterial diseases and become the new antibiotics. Antivitamins are a class of compounds that counteract the functions of vitamins. The study is published in the peer-reviewed journal Nature Chemical Biology. Origin of antivitamins The concept of antivitamins is quite old. Introduced sometime in the early 1900s, these compounds are present in food in some amount and counter the effects of vitamins. Studies suggest that the effects of antivitamins show up in the form of vitamin deficiency, which can be corrected by adding the required vitamin in the diet. Antivitamins K, B9 and B12 drugs are already used for their medical applications — stopping blood clotting, suppressing cancer and microbial growth. However, it is believed that the field has much more scope if explored. The recent study For a recent study, scientists studied the effects of naturally occurring antivitamin B1 on bacterial growth. Some bacteria present in our gut produce a toxic form of B1 to suppress the growth of competing bacteria around them. As per a news release by the University of Göttingen, this bacterial version of B1 has a single atom different from the original vitamin. Looking for how the antivitamin acts, the researchers found that it stops the ‘dance of protons’ in an important protein involved in the metabolism of E.coli. Dance of protons is a way by which distant areas in a protein interact with each other, which is like electricity in a wire. “Just one extra atom in the antivitamin acts like a grain of sand in a complex gear system by blocking its finely tuned mechanics," said the lead researcher Dr Kai Tittmann, professor of molecular enzymology at the University of Göttingen, in a news release. Interestingly, the antivitamin does not negatively affect the normal cells of the body. The researchers suggested that either the human proteins are not binding with this antivitamin or they are not affected by the binding. Nonetheless, the absence of any negative effects of this antivitamin on human cells makes it a good candidate for the development of antibiotics. For more information on antibiotics and antibiotic resistance, read our article on Antibiotics. Health articles in Firstpost are written by myUpchar.com, India’s first and biggest resource for verified medical information. At myUpchar, researchers and journalists work with doctors to bring you information on all things health.
Antivitamins K, B9 and B12 drugs are already used for their medical applications — stopping blood clotting, suppressing cancer and microbial growth
Advertisement
End of Article


)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)



