How often do you find yourself shivering when no one else around you is even feeling chilly? If not a lot, we’re sure you must have encountered people who feel a lot colder than others, without any discernible cause. They’re easy to identify, always bundled up in at least two more layers in comparison and usually found hovering close to any heat source available. Although feeling cold is a natural reaction of the body, feeling unusually cold could be a sign of an underlying medical condition. Let’s go over five such conditions which can make you cold intolerant. [caption id=“attachment_7866971” align=“alignleft” width=“380”]  Representational image. Image source: Getty Images.[/caption]
1. Hypothyroidism
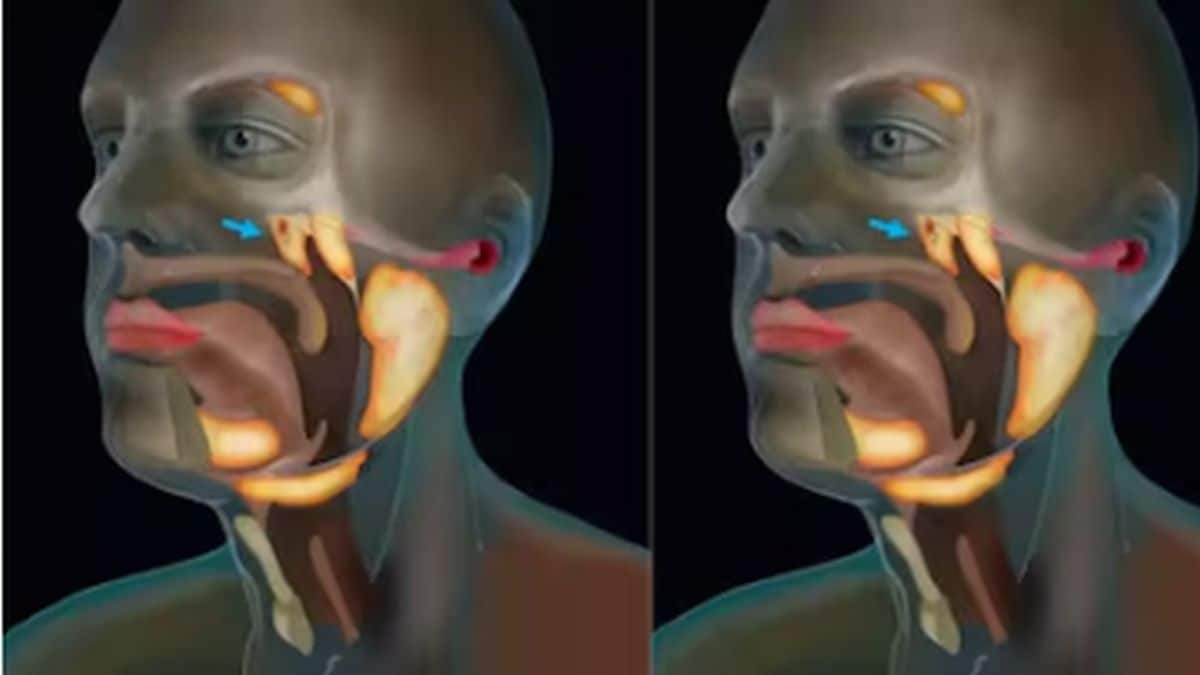
The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped gland present in the front of the neck just below Adam’s apple. It helps regulate many body functions (including metabolism and body temperature) by constantly releasing a steady amount of thyroid hormones into the bloodstream. Hypothyroidism is the state of decreased production of thyroid hormone in the body. Thus, a person suffering from hypothyroidism is more likely to be cold intolerant. Besides feeling cold, other symptoms of hypothyroidism are sudden weight gain, dry skin, constipation, fatigue and thinning of hair.
2. Anaemia
The red blood cells (RBCs) present in the blood carry oxygen throughout the body. Anaemia is a medical condition in which the body does not have enough RBCs in the blood. Anaemia can occur either due to less production of RBCs in the body, due to destruction of the RBCs or due to severe blood loss. With fewer RBCs in the blood, less oxygen circulates to the limbs making people feel colder, particularly in the hands and feet. Other symptoms of anaemia include pale skin, headaches, weakness, chest pain and fatigue.
3. Anorexia
Anorexia nervosa is an eating disorder in which people experience an intense fear of gaining weight and have a distorted body image. To lose weight they may intensely restrict their food intake, exercise excessively and compulsively or purge with the help of laxatives or by induced vomiting. People with anorexia can experience cold intolerance as they may have inadequate body fat. Anorexia patients may present with dramatic weight loss, a constant worry regarding weight, sleeping problems, dizziness, etc.
4. Raynaud’s disease
Raynaud’s disease is the condition where the small blood vessels in the extremities such as hands and feet (fingers and toes) become over-sensitive to even a minute change in temperature, mostly the cold. The hands may also get cold during stressful situations. Other symptoms of Raynaud’s disease include a change in the colour of hands or feet from white to blue or red, cold extremities, numbness and tingling or pain in hands or feet. Raynaud’s disease usually affects the hands and feet but it can also affect extremities like ears, nose, lips, tongue and nipples.
5. Artery disease
If enough blood is not reaching the extremities of the body then one may feel unusually cold in their hands or feet. Atherosclerosis is one of the reasons behind restricted blood flow to the extremities. In atherosclerosis, plaque gets accumulated on the artery walls making them narrower. This makes it difficult for the blood to flow through them. Therefore, due to reduced blood flow to the extremities, the hands and feet tend to get colder even after slight exposure to change in temperature. For more on this topic, please read our article on Hypothyroidism_._ Health articles in Firstpost are written by myUpchar.com, India’s first and biggest resource for verified medical information. At myUpchar, researchers and journalists work with doctors to bring you information on all things health.


)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)



